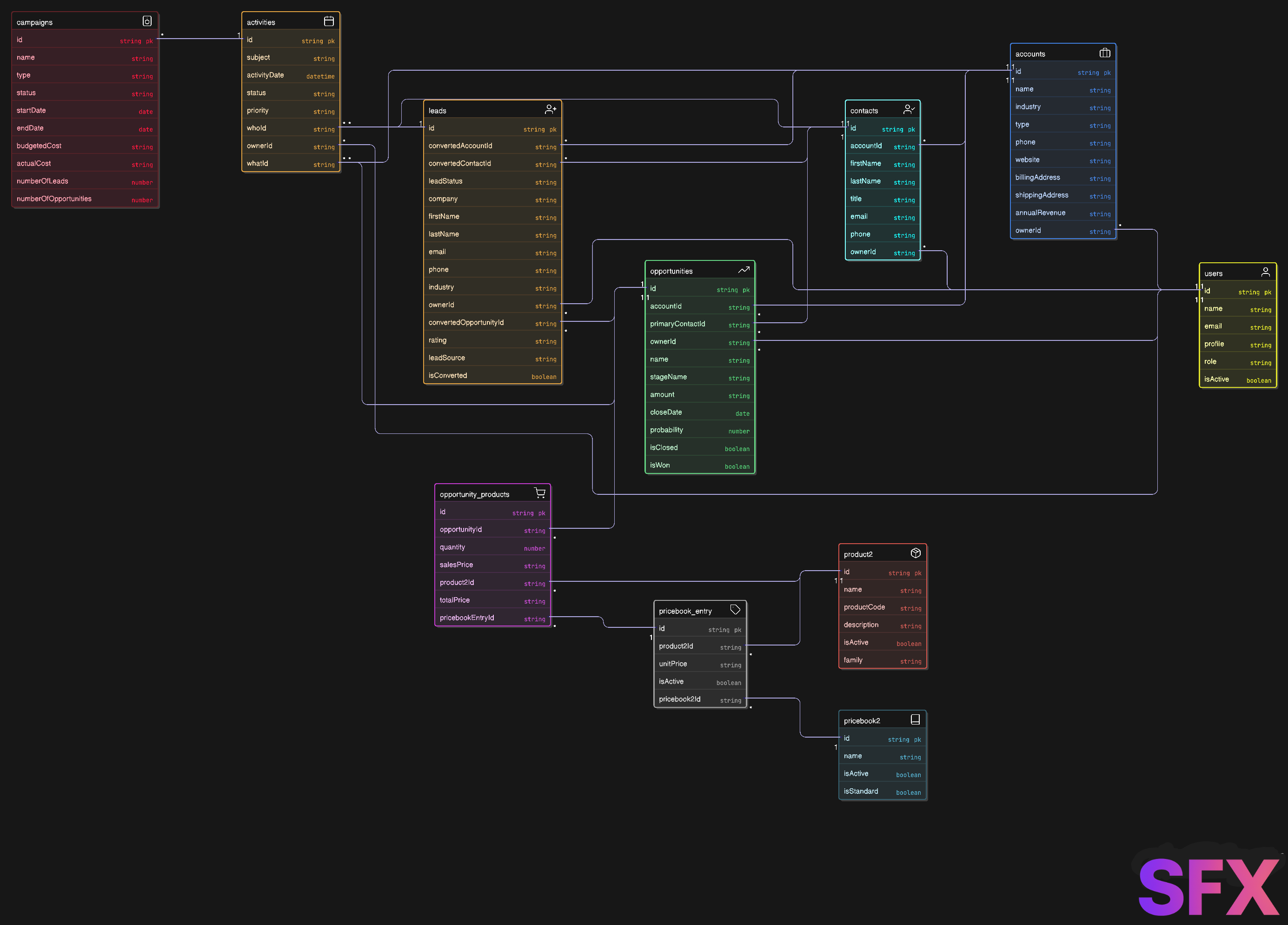
Salesforce Sales Cloud Conceptual Class Diagram
This page provides a formal, comprehensive reference for all key objects and relationships in Salesforce Sales Cloud, suitable for both architects and decision makers.
Contents
1. Standard Objects Overview
Salesforce Sales Cloud consists of these core objects. Each serves a distinct role in supporting the sales lifecycle:
| Object | Purpose | Key Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| User | Represents a Salesforce user (salesperson, manager, admin, etc.). | Id, Name, Email, Profile, Role, IsActive |
| Lead | Potential customer (person/company) not yet qualified. | Id, Company, Name, Email, Phone, LeadStatus, IsConverted, ConvertedAccountId, ConvertedContactId, ConvertedOpportunityId |
| Account | Business or organization you sell to. | Id, Name, Industry, Type, Billing/Shipping Address, Website, OwnerId |
| Contact | Individual at an Account. | Id, Name, Title, Email, Phone, AccountId, OwnerId |
| Opportunity | Potential sale/deal in progress. | Id, Name, StageName, Amount, CloseDate, AccountId, OwnerId, IsClosed, IsWon |
| Product2 | Product/service offered for sale. | Id, Name, ProductCode, Description, IsActive |
| Pricebook2 | List of products and their prices. | Id, Name, IsActive, IsStandard |
| PricebookEntry | Specific product-pricebook pairing and price. | Id, Product2Id, Pricebook2Id, UnitPrice, IsActive |
| OpportunityLineItem | Product added to an Opportunity (with quantity and price). | Id, OpportunityId, Product2Id, PricebookEntryId, Quantity, SalesPrice, TotalPrice |
| Campaign | Marketing initiative (email, event, etc.). | Id, Name, Type, Status, StartDate, EndDate, NumberOfLeads, NumberOfOpportunities |
| Activity | Task/Event related to records (calls, meetings, etc.). | Id, Subject, ActivityDate/StartDateTime/EndDateTime, Status, WhoId, WhatId, OwnerId |
2. Relationships Explained
- Lookup Relationship
- One-to-many, loosely coupled. Child can exist without parent. Example: Contact to Account.
- Master-Detail Relationship
- One-to-many, strongly coupled. Child (detail) cannot exist without parent (master). Roll-up summaries allowed. Example: OpportunityLineItem to Opportunity.
- Many-to-Many (Junction Object)
- Implemented with a junction object (e.g., CampaignMember links Campaign to Lead/Contact).
- Self & Hierarchical Relationships
- Object references itself (e.g., Parent Account), or special User management hierarchy.
- Special: Lead Conversion
- Business process: Lead is converted into Account, Contact, and Opportunity.
3. Automation & Business Processes
- Salesforce Flow: Automates lead nurture, assignment, approvals, and notifications.
- Einstein AI: Predictive lead scoring, opportunity forecasting, recommendations.
- Assignment Rules: Automatically route leads to the right reps/queues.
- Validation & Duplicate Rules: Ensure data quality and block duplicates.
- Roll-ups & Reporting: Summarize child records, visualize KPIs on dashboards.
4. Textual Class Diagram
User
└─ owns → Lead
└─ converts to → Account
├─ has → Contact
│ └─ can be → Opportunity.PrimaryContact
└─ has → Opportunity
└─ has → OpportunityLineItem
├─ refers → Product2
└─ refers → PricebookEntry
Pricebook2
└─ has → PricebookEntry
Campaign
└─ influences → Lead/Opportunity/Contact
Activity
└─ related to → Lead, Account, Contact, Opportunity
5. Conclusion
This formal class diagram and overview summarize the architecture and automation that make Salesforce Sales Cloud a leading CRM platform. Understanding these objects and relationships is key to building scalable, maintainable, and effective sales solutions.
For implementation or consulting support, contact SFX Support.
